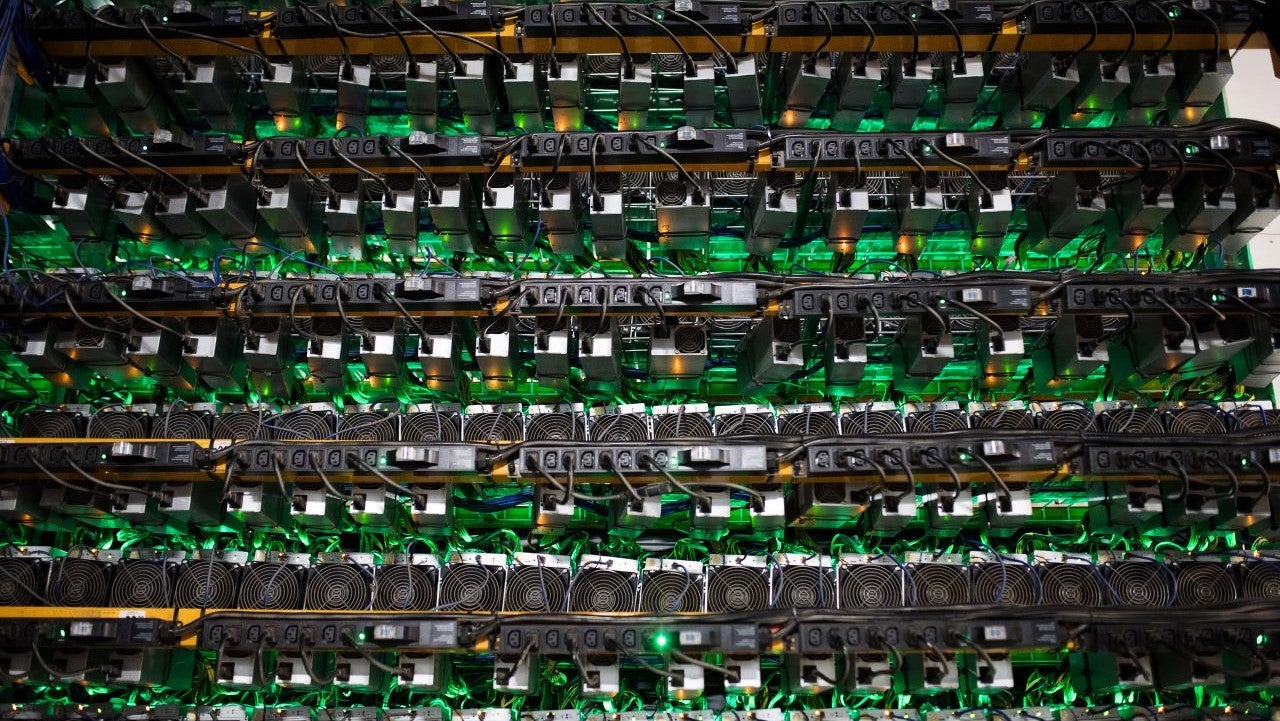
Bitcoin mining is the process of creating new bitcoins by solving extremely complicated math problems that verify transactions in the currency. When a bitcoin is successfully mined, the miner receives a predetermined amount of Bitcoin.
Bitcoin is one of the most popular types of cryptocurrencies, which are digital mediums of exchange that exist solely online. Bitcoin runs on a decentralized computer network, or distributed ledger, that tracks transactions in the cryptocurrency. When computers on the network verify and process transactions, new bitcoins are created, or mined. These networked computers, or miners, process the transaction in exchange for a payment in Bitcoin.
As the prices of cryptocurrencies and Bitcoin in particular have skyrocketed in recent years, it’s understandable that interest in mining has picked up as well. A miner currently earns 3.125 Bitcoin (about $334,375 as of mid-June 2025) for successfully validating a new block on the Bitcoin blockchain. But for most people, the prospects for Bitcoin mining are not good due to its complex nature and high costs.
Here are the basics of how Bitcoin mining works and some key risks to be aware of.
How Bitcoin mining works
Bitcoin is powered by blockchain, which is the technology behind many cryptocurrencies. A blockchain is a decentralized ledger of all the transactions across a network. Groups of approved transactions together form a block and are joined by computers within the network (called miners) to create a chain. Think of it as a long public record that functions almost like a long-running receipt. Bitcoin mining is the process of adding a block to the chain.
Bitcoin miners pick transactions from a group of unconfirmed transactions, called a mempool, to form a block on the blockchain. Before they can add the block securely to the blockchain, miners must solve what’s called a proof-of-work puzzle by guessing a number (also called a nonce). This number is combined with the block’s data and processed through a function called SHA-256.
The ultimate goal: create a block hash, which is a code with enough leading zeros to be less than, or equal to, the network’s target hash. The target hash is what determines how difficult the puzzle is to solve.
Target hash example: 0000000000000000ffff00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Block hash example: 0000000000000000057e29f1b57c1a9d5b90a6b7f1b4f0c9e2b0a1d3e4f5c6d7
Remember the block hash must be less than or equal to the target hash. Think of it like a dice game where the only way to win is if you roll a number smaller than or equal to a some number you’re given at the beginning. That number is made mostly of zeros, so you’d need a really insane and rare roll — a hash with tons of zeros in front of it — to win. In this example, the target hash’s “ffff” represents numbers that are non-zero and the block hash is less than the target hash, therefore solving the puzzle.
If you’re wondering whether this process requires a ton of computational power, you’re right. Miners use extremely powerful computers, called ASICs, to make billions — or trillions — of guesses about which nonces could work. One computer can cost up to $10,000. ASICs also consume huge amounts of electricity, which has drawn criticism from environmental groups and limits the profitability of miners. Technically, though, you could mine Bitcoin with, say, a MacBook Pro, but unfortunately you won’t get very far because there’s not enough computing power.
If a miner is able to successfully add a block to the blockchain, they will receive 3.125 bitcoins. The reward amount is cut in half roughly every four years, or every 210,000 blocks. As of mid-June 2025, Bitcoin traded at around $107,000, making 3.125 bitcoins worth $334,375.
Risks of Bitcoin mining
- Regulation: Very few governments have embraced cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, and many are more likely to view them skeptically because the currencies operate outside government control. There is always the risk that governments could outlaw the mining of Bitcoin or cryptocurrencies altogether as China did in 2021, citing financial risks and increased speculative trading.
- Price volatility: Bitcoin’s price has fluctuated widely since it was introduced in 2009. Since just January 2023, Bitcoin has at times traded for less than $18,000 and more than $110,000 recently. This kind of volatility makes it difficult for miners to know if their reward will outweigh the high costs of mining.
How to start Bitcoin mining
Here are the basic components you’ll need to start mining Bitcoin.
- Wallet
-
This is where any Bitcoin you earn as a result of your mining efforts will be stored. A wallet is an encrypted online account that allows you to store, transfer and accept Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies. Companies such as Coinbase, Trezor and Exodus all offer wallet options for cryptocurrency.
- Mining software
-
There are a number of different providers of mining software, many of which are free to download and can run on Windows and Mac computers. Once the software is connected to the necessary hardware, you’ll be able to mine Bitcoin.
- Computer equipment
-
The most cost-prohibitive aspect of Bitcoin mining involves the hardware. You’ll need a powerful computer that uses an enormous amount of electricity in order to successfully mine Bitcoin. It’s not uncommon for the hardware costs to run around $10,000 or more.
Bitcoin mining statistics
- Creating Bitcoin consumes 184.4 terawatt-hours of electricity each year, more than is used by Poland or Egypt, according to the Cambridge Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index.
- The price of Bitcoin has been extremely volatile over time. In 2020, it traded as low as $4,107 and reached an all-time high of $111,970 in May 2025. As of mid-June, it traded around $107,000.
- The United States (37.8 percent), Mainland China (21.1 percent) and Kazakhstan (13.2 percent) were the largest bitcoin miners as of December 2021, according to the Cambridge Electricity Consumption Index.
Taxes on Bitcoin mining
It’s important to remember the impact that taxes can have on Bitcoin mining. The IRS has been looking to crack down on owners and traders of cryptocurrencies as the asset prices have ballooned in recent years. Here are the key tax considerations to keep in mind for Bitcoin mining.
- Are you a business? If Bitcoin mining is your business, you may be able to deduct expenses you incur for tax purposes. Revenue would be the value of the bitcoins you earn. But if mining is a hobby for you, it’s not likely you’ll be able to deduct expenses.
- Mined bitcoin is income. If you’re successfully able to mine Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies, the fair market value of the currencies at the time of receipt will be taxed at ordinary income rates.
- Capital gains. If you sell bitcoins at a price above where you received them, that qualifies as a capital gain, which would be taxed the same way it would for traditional assets such as stocks or bonds.
Check out Bankrate’s cryptocurrency tax guide to learn about basic tax rules for Bitcoin, Ethereum and more.
Is Bitcoin mining profitable?
It depends. Even if Bitcoin miners are successful, it’s not clear that their efforts will end up being profitable due to the high upfront costs of equipment and the ongoing electricity costs.
Worldwide, bitcoin mining uses more electricity than Poland, a nation of 36.7 million people, according to the University of Cambridge’s Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index.
As the difficulty and complexity of Bitcoin mining has increased, the computing power required has also gone up. Bitcoin mining consumes about 184.4 terawatt-hours of electricity each year, more than most countries, according to the Cambridge index.
One way to share some of the high costs of mining is by joining a mining pool. Pools allow miners to share resources and add more capability, but shared resources mean shared rewards, so the potential payout is less when working through a pool. The volatility of Bitcoin’s price also makes it difficult to know exactly how much you’re working for.
Bottom line
While Bitcoin mining sounds appealing, the reality is that it’s difficult and expensive to actually do profitably. The extreme volatility of Bitcoin’s price adds more uncertainty to the equation.
Keep in mind that Bitcoin itself is a speculative asset with no intrinsic value, which means it won’t produce anything for its owner and isn’t pegged to something like gold. Your return is based on selling it to someone else for a higher price, and that price may not be high enough for you to turn a profit.
— Bankrate’s Logan Jacoby contributed to an update of this article.
Why we ask for feedback
Your feedback helps us improve our content and services. It takes less than a minute to
complete.
Your responses are anonymous and will only be used for improving our website.
Help us improve our content
Read the full article here